Strategic Deworming of the Beef Herd: Continuing the Resistance Fight
Strategic Deworming of the Beef Herd: Continuing the Resistance Fight
by Nancy Glazier, NWNY Dairy, Livestock, and Field Crops Program
What are internal parasites?
Internal parasites are gastrointestinal worms that infect cattle. Cattle shed eggs on pasture where they hatch, and larvae grow through stages. At the L3 stage, larvae crawl up plant stems and become ingested by cattle where they mature and overwinter. They lay eggs in the spring and the eggs are shed back on pasture.
How do I know if my cattle has internal parasites?
Cattle can look unthrifty and have poor gain. Before there are visual signs production losses may have already occurred. Even low populations can impact gain and milk production. Fecal egg counts (FEC) are necessary to assess parasite load.
Fecal egg counts are determined from a 'clean' manure sample. Rectal or freshly dropped samples should be collected. The sample is weighed, and eggs are floated in a solution to give an egg count per gram (typically) sample.
How can I tell if my cattle have resistant worms?
To check for resistance Fecal Egg Count Reduction (FECR) tests are recommended. Manure samples are collected at the time of treatment and then resampled 14 days later. The recommendation is to test the same cattle, minimum of six, if possible 10-15, from the same class or life stage both times. What has been found, 80% of the worms may be in 20% of the cattle. Your veterinarian may be able to assist with testing. Other options include Cornell Animal Health Diagnostic Center (https://ahdc. vet.cornell.edu/) or commercial labs. One I have worked with is MidAmerica Ag Research (https:// midamericaagresearch.net).
This method has drawbacks depending on the time of the year. There may be immature nematodes in the intestines or abomasum that may not be egg laying which may show inaccurate numbers. Worms become dormant in the winter and mature and begin reproduction in late spring.
How do I control worms?
Strategic deworming recommendations are revised as new information is evaluated. From recent presentations from Dr. Christine Navarre, Louisiana State professor/veterinarian, there are two strategies: targeted selective treatment and selective non-treatment; both treatments need to be tailored to your farm. With selective treatment only animals that will most benefit will be treated. They include calves, young females, and bulls. Depending on breed no adult cows should be treated after weaning their first calf. If they are wormy, they should be culled to remove those genetics from the herd.
For selective non-treatment: if your herd is segregated - cows are kept separate from young or after weaning - treat the bottom 90% of the group of replacement heifers or calves. Leave the heaviest onesuntreated. Another suggestion is to treat 9 out of 10 animals unless the 10th is unthrifty; treat and skip the next.
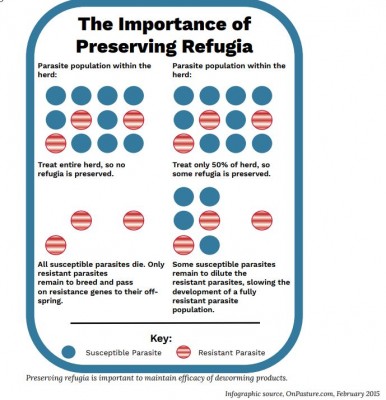
With both strategies some cattle are left untreated to provide refugia, where worms have had no exposure to dewormers.
It is also recommended to treat with two different classes of dewormers concurrently, but not mixed.
- Macrocyclic lactones (Ivomec, Dectomax, Cydectin, etc.)
- Benzimidazoles (Valbazen, Safeguard, Synanthic, etc.)
- Imidazothiazoles / Tetrahydropyrimidines (Levasole, Tramisole, Rumatel, etc.)
Dose calves based on actual weight, or on the heaviest. Use pour-on products cautiously; dosage may be impacted by rain, rubbing, or licking. Don't deworm in feed or mineral, and properly store the products. Thoroughly read the label.
Pasture management is vital for parasite management. Ideally, pastures should be rested 3 months. Do not graze pastures shorter than 4 inches. Limit access to pastures that are wet. Some further guidelines include:
- Increase overall herd immunity
- Proper nutrition
- Decrease other stressors/diseases
- Do not buy resistant worms (from purchased animals)
- Cull cows that are not thriving in your environment
- Use hybrid vigor!
Your veterinarian can help you develop your strategic deworming plan for your farm to meet your production goals
Gastrointestinal Parasites Fact Sheet - PDF (pdf; 1033KB)
Upcoming Events
WNY Pastureland Conversion & Soil Health Field Day
July 16, 2025
Middleport, NY
Join American Farmland Trust for the Western New York Soil Health Field Day on July 16, 2025, at Zeliff Farm in Middleport, NY, from 9:00 AM-3:15 PM. Learn about pasture conversion, soil health benchmarking, biochar in grazing systems, and best grazing practices. Plus, enjoy hands-on demos with the NY Soil Health Trailer, drones, and cover crops! Check out the attached agenda for more information about the field day and REGISTER HERE. Zeliff Farms is a regenerative beef operation who has recently partnered with AFT on outreach and education to farmers including learning circles and evaluating biochar effects on soil health.
IPM Strategies to Protect Corn and Soybean Seed in NY
July 30, 2025
Hamburg , NY
SWNYDLFC and Cornell IPM are hosting a grower meeting to discuss integrated pest management strategies for protecting corn and soybean seed in New York.
FAMACHA Training for Sheep and Goat producers in Woodhull NY
August 13, 2025 : FAMACHA Training in Woodhull
Woodhull, NY
Join us for a discussion and hands-on training for internal parasite integrated pest management in sheep and goats. Certification is available to all students participating in the workshop.
Announcements
No announcements at this time.





